Manufacturing Website Design Trends for 2026
Explore what's trending in website design for manufacturing companies as the industry and the web are both rapidly changing in 2026.
If you're a manufacturing business that still treats your website like a glorified online brochure, you're playing with fire.
In the midst of whiplash-inducing tariffs, brittle supply chains, outsourcing, reshoring, and other challenges, the smartest industry players have turned their websites into command centers.
Web-based digital platforms aren't just branding, they're lifelines. Websites are doing the work of entire departments, providing real-time updates, integrated support portals, and dynamic inventory visibility.
They're how manufacturers stay agile in the face of policy chaos and global uncertainty, and how they prove stability when everything else feels volatile. Ignore this evolution and risk looking obsolete. Trust is earned, click by click. Your website is either your credibility or your liability.
Despite market headwinds, companies are doubling down on digital strategies. A recent Deloitte outlook noted that manufacturers are bolstering their digital and data foundations to navigate economic pressures.
They offer a stable interface for partners and customers even as back-end operations flex to meet new demands. And with the SQDC framework gaining ground (safety, quality, delivery, cost), modern manufacturing websites aren’t just checking a box.
"B2B buyers do 12 searches before they call. Your website better answer their questions or someone else's will. ~ Steve Fowler, Director of Client Marketing at DBS Interactive "
A manufacturing website is the front door to a company’s resilience strategy. A clear path to confidence. A signal that you’re built to withstand whatever hits next.
They’re the front door to a company’s resilience strategy. A clear path to confidence. A signal that you’re built to withstand whatever hits next.
The industrial website trends we’re seeing in 2026 reflect how manufacturers are turning economic uncertainty into motivation, ramping up their digital game, and leaning hard into transformation. Even with market headwinds, the pivot toward smarter, more strategic web design is anything but slowing down.
2026 Trends in Manufacturing Website Design and Development
Manufacturers face challenging demands in 2026 for websites that do much more than inform. They must engage visitors, convert them into sales leads, and adapt to web users' needs.
From high-impact interactive tools to AI-driven personalization, modern web development in manufacturing is blending innovation with strategy to deliver digital platforms that drive results. Here’s how leading companies are building smarter, more powerful manufacturing websites in 2026.
1. Engagement-Driven Experiences
A notable trend for manufacturing websites is the shift from basic customer portals and product listings to immersive, engagement-driven experiences.
Manufacturers are reinventing their websites as always-on digital showrooms, places where prospects can interact with products and content as if they were at a trade show or on a factory tour. Instead of just presenting specs and forms, sites now use 3D product visuals, virtual tours, and interactive demos to showcase complex equipment online.
For example, some industrial firms incorporate 3D models that visitors can rotate and explore, or augmented reality views of machinery in a plant setting. These rich media elements create a compelling showroom feel, helping to bridge the gap when in-person demos are costly or impossible.
This engagement-focused approach reflects a broader B2B trend: buyers want the informative, visual experience of B2C e-commerce even for high-stakes industrial purchases.
Studies show B2B buyers conduct extensive online research (averaging 12 searches) before even contacting suppliers.
Manufacturers are responding by providing self-service content that educates and engages.
For instance, an OEM’s site might feature an interactive product configurator (to customize a part or machine), alongside virtual walkthroughs of its production line for transparency.
Similarly, distributors are rolling out rich online product catalogs with comparison tools and AI-driven search, making it easier for engineers and procurement managers to find the right product and feel confident in its capabilities.
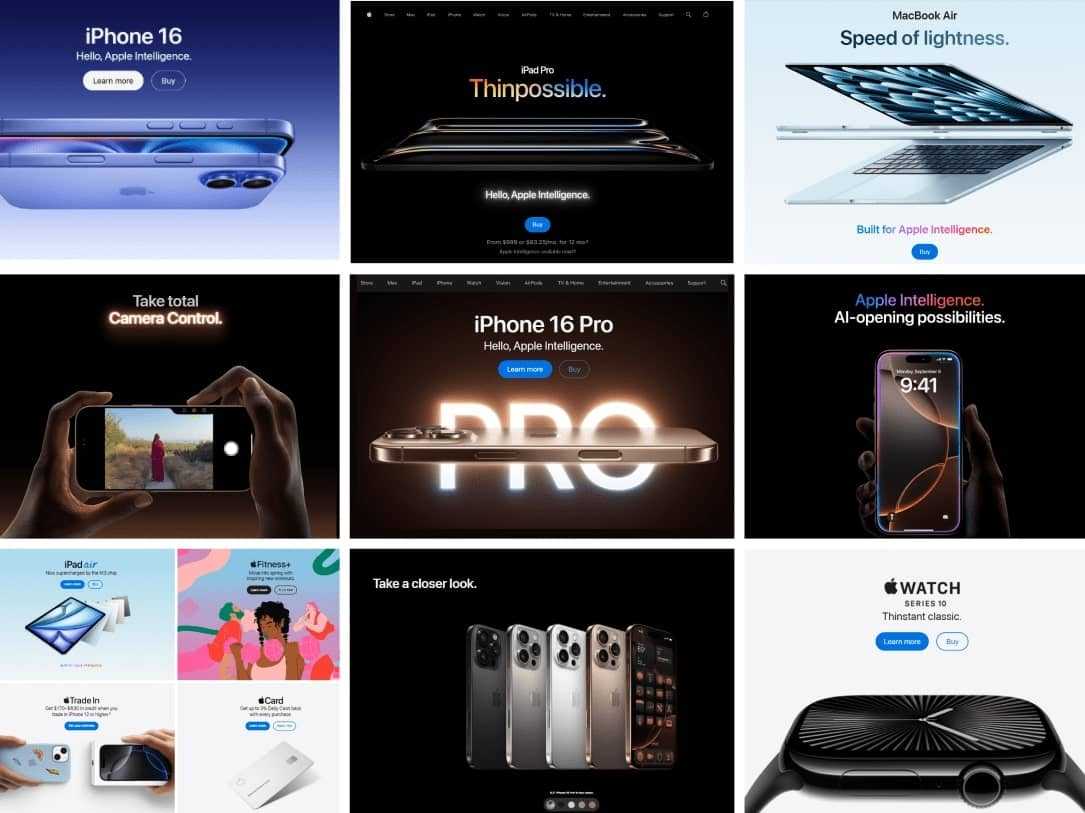
Crucially, these digital showroom elements turn passive browsing into active exploration. Rather than a flat portal where users simply log in to place orders, the modern manufacturing website invites visitors to experience the brand’s expertise.
Engaging video case studies, customer testimonial sliders, and even scrollytelling pages help tell a story as the user scrolls, weaving narrative with visuals and data. Scrollytelling (scroll-driven storytelling) has gained popularity in B2B web design, as it can break down complex information into a flowing, narrative format.
A long homepage might start with a bold overview and then reveal deeper details, case studies, and technical specs as the user scrolls, mimicking a guided tour. This approach keeps users engaged longer and conveys more information without overwhelming them at first glance.
The bottom line is that in 2026, manufacturing websites are no longer just transaction enablers – they’re experience platforms. Every page is an opportunity to engage and inform. Even traditionally dry sections like parts catalogs or customer portals are being reimagined with richer visuals and interactivity to keep buyers interested.
This engagement-centric mindset is especially critical amid economic uncertainty, as manufacturers vie to turn web visitors into long-term customers with a persuasive, content-rich online presence.
2. AI-Powered Content, Search, and Personalization
Another game-changer for industrial websites in 2026 is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) across content creation, site search, and personalization features. AI’s influence on the website can be observed in various ways.
Intelligent Content Creation
Manufacturing marketers are increasingly leveraging generative AI tools to produce and optimize website content. In 2024, an estimated 85% of marketers reported that AI changed how they create content, and 64% are already using AI for content creation.
For manufacturers, this might mean using AI to draft technical blog posts or product descriptions, which human experts then refine for accuracy. It speeds up content production while ensuring consistency.
AI can also analyze which content resonates with different buyer personas and suggest topics to fill information gaps. The result is more relevant content at scale, tailored to what B2B buyers are searching for.

Enhanced Site Search and Product Discovery
AI-driven search functionality is transforming the usability of large manufacturing catalogs.
Traditional site search often struggles with complex part numbers or engineering terms. New AI-powered catalog search can understand natural language queries and deliver precise results.
Some sites feature chatbot-style search interfaces, where an AI assistant helps users find the right product or technical documentation by asking follow-up questions.
These AI catalog tools use machine learning on past queries and purchase data to improve accuracy over time. They can also offer recommendations, effectively upselling in a helpful way.
Personalization and AI Recommendations
Perhaps the most impactful AI trend is personalization. Today’s B2B buyers expect the same kind of tailored experience they get on consumer sites. In fact, 80% of business buyers are more likely to buy from a company that provides personalized experiences.
Manufacturers are meeting this expectation by using AI to dynamically personalize content. A returning visitor from the automotive industry, for example, might automatically see auto-relevant case studies and products featured on the homepage, as the site recognizes their industry segment.
AI can segment visitors by firmographic data or behavior, then serve up relevant white papers, videos, or even pricing information tailored to that segment. This level of personalization keeps users engaged by presenting exactly the content they need, rather than a one-size-fits-all approach.


AI Chatbots for Support
Another common feature is the deployment of AI chatbots and virtual assistants on manufacturing sites. In 2024 alone, over half of B2B marketers had integrated AI chatbots into their demand generation programs.
On an industrial website, a chatbot provides instant support and captures leads by prompting visitors to ask questions or schedule demos. These bots can handle frequently asked questions and guide users to resources 24/7.
Modern AI bots are far more context-aware than old rule-based ones. They interpret a user’s question, even if phrased informally, and pull answers from a knowledge base or the website content.
This is especially useful for complex technical queries, effectively offering visitors a virtual sales engineer on the site at all times.
All these AI applications contribute to a more user-centric and efficient experience. Buyers find what they need faster, through smart search and chat, and they feel understood thanks to personalization. From the business side, AI analytics can also uncover patterns such as which content leads to the most RFQs, helping manufacturers continuously refine their web strategy.
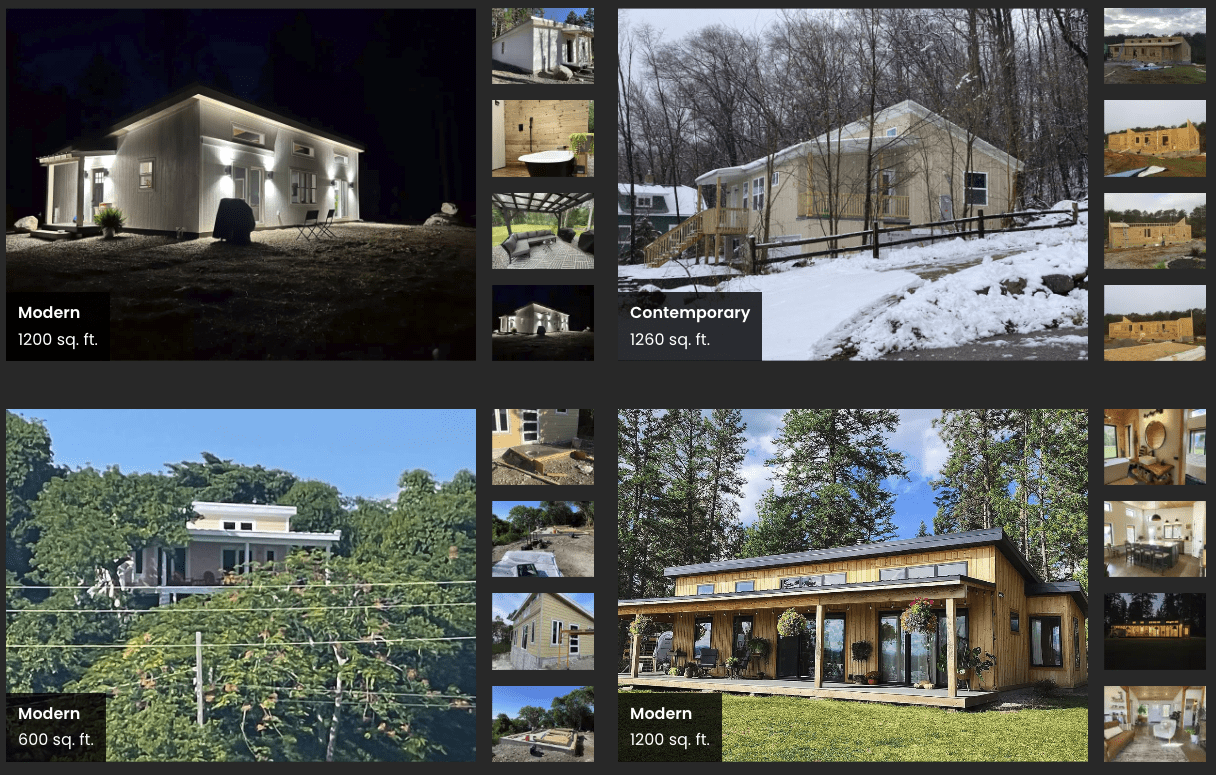
How Mighty Big Dreams Come to Life
Mighty Small Homes wanted to showcase the hundreds of inspiring photos customers shared of their home-building projects. DBS delivered a clean, dynamic grid layout that beautifully organizes these images for easy browsing.
3. Modernizing the Website’s Design and UI
Aesthetics and usability go hand in hand in 2026’s top web design trends. Manufacturing websites are adopting modern UI design principles that make content easier to consume and more visually appealing, without sacrificing the professionalism B2B brands require. Three notable design elements are grid layouts, visual depth effects (like glassmorphism), and micro-interactions.
-
Dynamic Grid Layouts: Grid-based layouts have become a go-to design structure for industrial sites, especially on homepages and product listing pages. By arranging content in clean cards or tiles, a grid layout brings order to potentially dense information.
Each “grid” item can hold a product photo, title, and key details, making it easy for users to scan a lot of offerings at once. This is particularly popular for product catalogs and spec sheets, where a dynamic grid presents multiple product families on one screen in a responsive way.
"A well-crafted grid balances order and creativity, delivering an efficient user journey while keeping the design fresh and engaging," said Mark Shelton, Chief Operations Officer at DBS Interactive, a Louisville-based digital agency in Kentucky.
Grids also lend themselves to asymmetrical designs for added visual interest, for example, alternating wide and narrow columns to highlight certain content. According to web design experts, this trend toward compartmentalized, grid-based pages allows users to digest information quickly and find what they need with minimal scrolling. It’s a direct response to busy B2B visitors who want efficiency.
-
Glassmorphism and Visual Depth: Visually, many B2B sites are moving past flat design and incorporating subtle depth effects like glassmorphism, a style that uses translucent, “frosted glass” backgrounds and soft shadows, to layer content. In a manufacturing context, glassmorphic elements can add a high-tech feel to a page, evoking the look of modern software interfaces.
For instance, a hero banner might feature text on a semi-transparent overlay that blurs the background image slightly, creating a sense of depth. This trend, along with other neumorphic or material design touches, helps industrial websites appear up-to-date and innovative.
It’s often combined with vibrant gradient colors or imagery to catch the eye.
The key is restraint.
Used sparingly for navigation menus, cards, or callout boxes, these effects make a site feel contemporary and polished without compromising readability. They also align with manufacturers’ broader branding efforts to be seen as cutting-edge and digitally savvy.
-
Micro-Interactions and Animated Feedback: While big imagery and layouts get attention, it’s the small details that often elevate the user experience.
Micro-interactions are those subtle animations or responses a site gives to user actions, like a button that gently shimmers on hover, or a form field that shakes if the input is invalid. These may seem minor, but they play a huge role in making interfaces feel alive and intuitive.
In 2026, we see B2B designers paying close attention to these details. For example, when a user adds a product to a quote request list, a tiny animation might show it dropping into a cart icon, providing satisfying feedback. A download link could have a progress bar or spinner icon while the PDF loads, reassuring the user that something is happening.
As Clear Digital notes, micro-interactions “enrich the overall experience” and make interfaces more intuitive by providing instant feedback. Manufacturing sites use them to keep users engaged during potentially tedious actions – one cited example is a cascading loading indicator on a parts catalog that entertains the user briefly while the content loads.
Beyond these, other visual design trends include bold typography (big, concise headlines to grab attention, a “less is more” approach to copy) and kinetic typography (animated text, which some forward-thinking sites use in hero sections to tell a story with moving text. Design must support the user experience purposefully.
Driving Global B2B Sales and Brand Awareness
Kao Collins aimed to dominate traditional search rankings and emerging AI answer results. See how we combined high-performance SEO, structured content, and a dynamic multichannel strategy to capture B2B buyers.

4. Optimizing Content for AI-Powered Search
As search engines incorporate AI and conversational features, manufacturers must adapt how they structure content for optimal visibility. Traditional SEO remains vital, but 2026 introduces new considerations to support AI-driven results and conversational search queries.
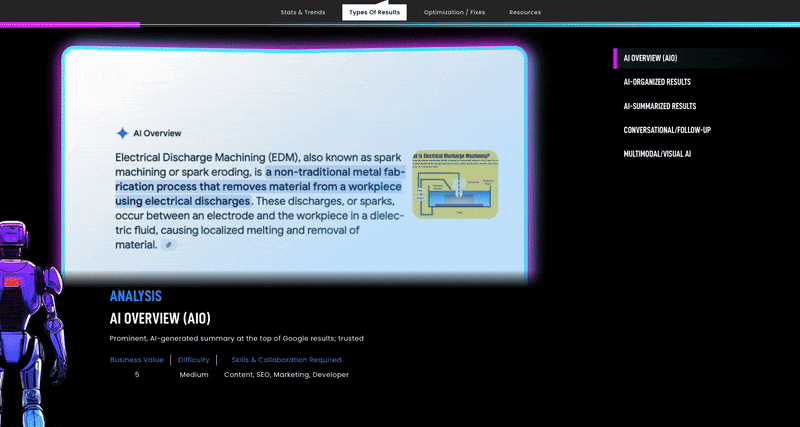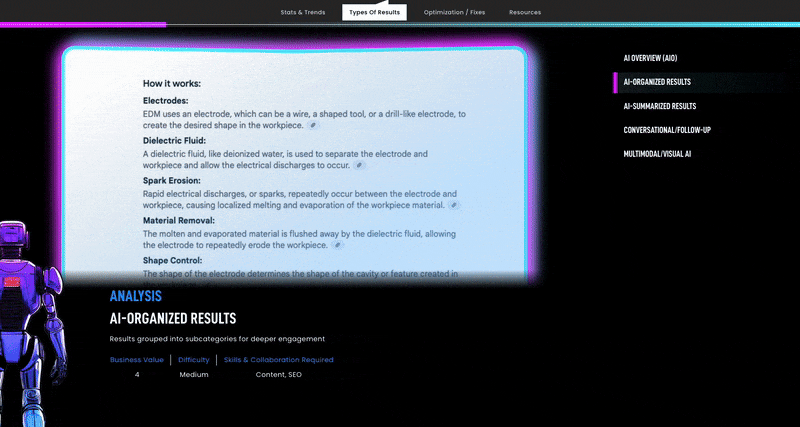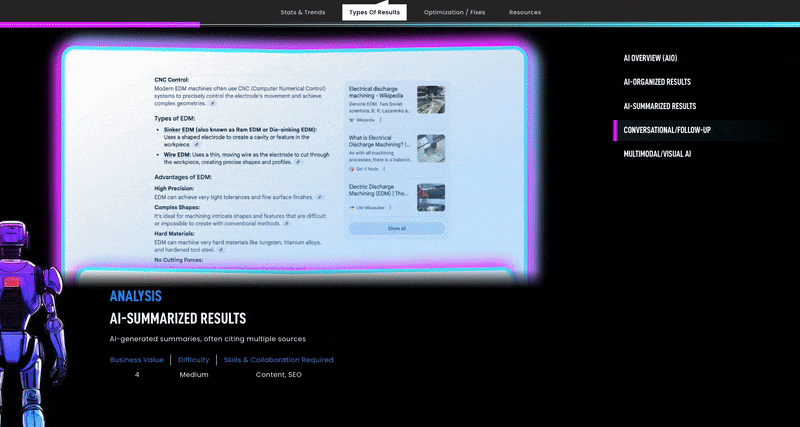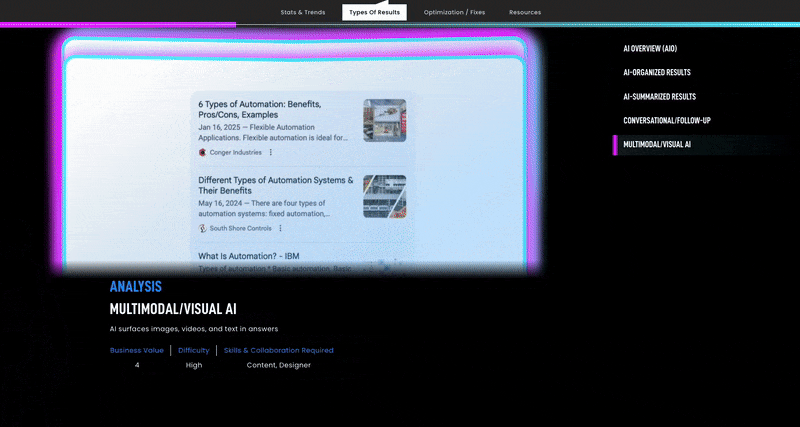
One big development is Google’s AI Answers and similar AI answers, which attempt to answer complex questions directly on the results page. This requires another aspect of SEO called AISO for artificial intelligence search optimization.
"Think less like a brochure, more like a sales conversation, because that’s exactly how people are now searching on Google and ChatGPT," said Steve Fowler, Marketing Director at DBS.
For example, a user might ask an AI-powered search, “What’s the best material for automotive gear housings, and who manufactures them?” Instead of just ten blue links, the AI will synthesize an overview and might cite specific manufacturers.
Manufacturers must increase the chances of being featured in these AI results, or at least make it more likely their website content will be cited as a source that the AI aggregates and uses to answer sales-driven prompts.
“Think less like a brochure, more like a sales conversation.” - Steve Fowler
AI Search Optimization Tips for Manufacturing Websites
Structure content clearly. Well-structured, semantically marked-up content is easier for AI to siphon into answers. Using proper headings, bullet lists, and Q&A formats on your site can make it more “AI-readable.” In fact, Google recommends using structured data that matches your page content to help its systems understand and feature your pages in rich results.
Use conversational content and FAQs. Since users are literally asking questions in search now, similar to meeting with a sales rep, manufacturing websites should adapt by publishing content that directly answers common questions. This means expanding your knowledge base and blog to cover not just product info, but also broader industry questions.
Incorporating an FAQ section, as we do at the end of this article, is also a smart move. FAQs on your site improve user experience, and they are also primed for voice search and conversational search snippets.
Optimize for conversational phrasing and natural language. Traditional SEO focused on short keywords like “CNC milling machine manufacturer.” Conversational search optimization means considering longer, more natural phrases: “Who makes custom CNC milling machines in the US?” or “best CNC machines for aluminum.” Manufacturers should update their SEO strategy to include these query phrases in their content, perhaps in an FAQ or in headings. The goal is to align with the way questions are phrased. Research shows conversational search is growing as generative AI gets integrated into search engines.
Don't forget Technical SEO fundamentals. Alongside these new tactics, don’t neglect the basic requirements that still drive AI visibility and performance. Ensure your site is crawlable and indexed properly, as technical issues could prevent your great content from being seen by search bots in the first place. Page speed, mobile-friendliness, and security are table stakes for techncial SEO and, by extension, for AI ranking.
Manufacturers should treat AI-powered search as an extension of SEO, not a replacement.
Clarity drives visibility. When your content answers buyer questions in research, meetings, and search, it climbs fast. In 2026, AI won’t just pick a link. It’ll pick a leader. Make sure that voice is yours.
5. Tailoring the Website to OEMs vs. Distributors
It’s worth noting that manufacturing covers a spectrum of business models, from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) selling complex systems to B2B/D2C distributors selling parts and supplies, and everything in between.
The latest web design trends manifest slightly differently depending on the type of manufacturer represented by the website.
-
OEM and Industrial Component Manufacturers: These companies often have longer sales cycles and smaller target audiences. Their websites in 2026 emphasize rich technical content and lead nurturing. Trends like digital showrooms for product lines, in-depth case studies, and personalization by industry are especially valuable here.
An OEM site might have a gated content library that uses personalization, for example, showing relevant documents based on the visitor’s industry selection. OEMs also focus on thought leadership in web content to build trust.
Expect to see more OEM sites running content hubs or blogs that discuss industry innovations, demonstrating expertise beyond just their product catalog. The design tone is usually a bit more conservative and brand-heavy to instill confidence, but as mentioned, even these sites are embracing modern UX elements like animations and scrollytelling to convey complex value propositions in a digestible form.
-
B2B2C Distributors and D2C E-Commerce Manufacturers: Manufacturers that sell via distribution or directly to small businesses and consumers have websites that borrow heavily from B2C and B2B e-commerce trends.
For instance, a distributor website selling industrial supplies might highlight a smooth e-commerce experience with advanced filtering, one-click reorders, and even ratings and reviews on products. These sites lean into grid layouts for product listings because they may have thousands of SKUs to present.
User-generated content, like reviews or Q&As, play a role in B2B Catalogs, which are common in consumer sites. Since price competition can be a factor, these sites also invest heavily in SEO, expecting a large volume of search-driven traffic. We see B2Bs adopting features like live chat sales support, personalized product recommendations (“Recommended for you” based on browsing history), and even loyalty programs via the website.
B2C e-commerce sites use vibrant, promotional visuals like sales banners and product highlights to drive conversion. OEM websites take a more restrained approach, but deliver exactly what B2B buyers need: Technical specs, comparison tools, and clear data remain front and center to support fast, confident decisions.
-
Custom Machinery and B2B Services: Many manufacturers offer more than just off-the-shelf products. Instead, they specialize in custom solutions and services such as contract manufacturing, equipment integrations, or application engineering. In 2026, these manufacturers will look to focus the website experience on immersive storytelling and credibility.
Site visitors will see trends like full-page video backgrounds showing factories in action, interactive timelines of production or processes, and prominent case studies with visualized metrics. Personalization here might mean tailoring the messaging to different sectors they serve, much like OEMs.
Manufacturing websites might lean on using more interactive content, such as ROI calculators or diagnostic quizzes. These interactive tools both engage the user and capture lead information, aligning with the manufacturer's longer sales cycle and consultative approach.
Powering Ahead for Growth
Blue Diamond Attachments had a vision to transform their digital presence into a cornerstone of business success that outshined competing OEMs. See how we delivered.

Despite these differences, one unifying theme across all manufacturing websites is the push for personalization and immersive engagement. Whether you’re a niche OEM or a broad-line distributor, the 2026 website is all about meeting the user where they are in their journey and making a memorable impression.
While the features and tone may vary, the goals remain consistent. Teams prioritize strong user experience, maximize search visibility, and drive engagement across every touchpoint.
6. Dark Mode, Sustainable UX, and Predictive Insights
Looking ahead, there are a few emerging web design trends worth briefly noting as they gain traction in the industrial space.

Dark Mode and Theming: Dark mode has swept across apps and operating systems, and now websites are catching up by offering dark theme toggles. A surprising 82% of smartphone users now use dark mode at least some of the time, and many prefer websites that can adapt accordingly.
Manufacturers are beginning to include a dark mode option on their sites, recognizing that engineers working late or users in low-light settings may switch to dark backgrounds to reduce eye strain.
Offering dark mode, while ensuring your site logo and colors work on it, can subtly signal that your company is modern and cares about UX preferences. It’s also part of a broader trend of user-controlled theming, allowing visitors to choose light/dark or even adjust text size easily for comfort.
Sustainable Web Design (Green UX): Sustainability isn’t just a manufacturing process goal; it’s entering web design. Sustainable UX involves optimizing websites to consume less energy and data, which is better for the environment and for user experience. Faster sites require less power.
This can mean using efficient coding practices, compressing images, and avoiding autoplay videos or bloated scripts that drain resources. Some manufacturing companies now highlight their lightweight websites as part of their corporate sustainability efforts, which is an interesting twist.
For example, using more black or dark colors in a site design can actually save battery power up to ~9-15% on OLED screens. While the impact of one website is small, collectively, the digital carbon footprint matters.
We anticipate “green” web design principles gaining more prominence, such as providing low-bandwidth site versions or simply designing clean, no-frills pages that load with minimal CPU usage. These principles align well with manufacturers’ overall push for efficiency and could even marginally improve SEO since faster sites rank better.
Predictive Sourcing Insights: In B2B manufacturing procurement, data is king. One emerging concept is integrating predictive insights into the web experience. Imagine a scenario where a logged-in customer visits a parts supplier’s portal and sees AI-generated forecasts like, “Based on your purchase history, you may run out of Item X in 2 weeks. Order now to avoid downtime.” This kind of predictive sourcing insight uses AI analytics on the customer’s data to provide proactive recommendations.
While still in early stages, some advanced B2B platforms are exploring these features. It’s essentially bringing the power of predictive analytics, common in supply chain software, directly into the website UX.
A simpler variant shows trends like “Most OEMs order extra consumable Y after 6 months; would you like to add one? during checkout.” As trust in AI grows, manufacturers could differentiate by making their sites a source of actionable intelligence for their customers. This strengthens the buyer-supplier partnership and can lock in loyalty.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Product Previews: Another emerging trend is AR integration. Using a phone, a user could go to a manufacturer’s product page and activate an AR preview, for instance, seeing how a piece of equipment would fit in their facility through their camera. While more prevalent in consumer retail, like seeing furniture in your room, AR for industrial use is on the horizon as the tech becomes more accessible via the web (WebAR). This ties into the digital showroom concept and 3D visuals mentioned earlier, pushing it a step further.
Each of these nascent trends – dark mode, sustainable UX, predictive analytics, AR – points to the continuous innovation in web design for manufacturers. They show that industrial websites are not standing still. Manufacturers are adopting the latest ideas from across tech and design. Those who experiment early with these features can position themselves as industry leaders and delight their users in novel ways.
Taking Next Steps with Your Manufacturing Website
By embracing the manufacturing website trends above, B2B manufacturers can ensure their websites deliver consumer-grade UX for complex buying processes, support modern SEO and discovery methods, and engage buyers on a deeper level.
From big themes like AI and personalization to design touches like micro-interactions, the common thread is a focus on the user’s experience and success. A well-designed site not only attracts visitors; it guides them smoothly toward solutions and strengthens their confidence in your brand.
Given that as much as 67% of the buyer’s journey is now done digitally in B2B, a modern manufacturing website is arguably one of your most important sales tools. The year 2026 will reward industrial businesses that invest in making these tools more effective, informative, and innovative using emerging technologies and trending features.
Close Sales with a Superior Website Design
You’ve modernized production. Now modernize how you sell it online.
FAQs
Manufacturing websites can do this by simplifying and streamlining the online purchase process – for example, using intuitive dashboards, smart search, and guided workflows that resemble consumer e-commerce. Features like one-click reorders, saved favorite lists, and real-time chat support can make a complex B2B order feel as easy as a consumer checkout.
A grid layout design structures content in a two-dimensional grid of rows and columns. In product catalogs, grid layouts are popular because they present many items in a neat, scannable way. Each product can be featured in its own “card” with a photo, name, and key specs or a brief description. This makes it easy for buyers to compare options at a glance without excessive scrolling.
Micro-interactions are the small feedback cues and animations a user interface provides in response to user actions. Examples include a button changing color on hover, a subtle loading spinner, or a form field shaking if the input is invalid. These might seem minor, but this kind of interactive content improves the user experience for manufacturing prospects by making the interface feel responsive and providing instant feedback. In a B2B context, micro-interactions guide prospects through complex knowledge-gathering and decision-making processes.
Personalization is crucial because B2B buyers now expect the same relevant, tailored experience online that they get in other aspects of their digital lives. In manufacturing, the B2B customer journey often involves prospects seeking a lot of detailed information. So rather than forcing prospects on manufacturing websites to sift through irrelevant content to find what they personally need, automating website personalization helps cut through the noise by showing them the content and features that are most specific to their needs.
To optimize for AI-driven search results, like Google’s conversational answers or voice queries, manufacturers should focus on structured, high-quality content that directly addresses common questions. Practically, this means adding FAQ sections, how-to guides, and knowledge base articles that use natural language questions and answers, the same way a user might ask via Alexa or Siri. Implementing structured data schema markup is also important, such as FAQ schema that helps search engines identify Q&A content on your site and feature it in rich results.
Modern manufacturing sites should incorporate a range of accessibility features to ensure users of all abilities can use the site effectively. Key features include:
- High Contrast Mode: Providing sufficient contrast between text and background, and even an optional high-contrast toggle, so that users with low vision or color blindness can read content clearly.
- Alt Text and ARIA Labels: All images, especially important diagrams or product photos, should have descriptive alt text for screen readers. Interactive elements should have ARIA labels where needed to explain their function to assistive tech.
- Keyboard Navigation: The site should be fully navigable using a keyboard alone, allowing for tabbing through menus, links, and form fields. This benefits users who can’t use a mouse. Visible focus indicators, outlines showing which element is selected, are essential here.
- Resizable Text: Users should be able to zoom in or increase the text size without breaking the layout. Relative font sizes and responsive design help accommodate this.
- Captioning/Transcripts: If you have videos (like product demos or webinars), include captions or provide transcripts so hearing-impaired users or those who prefer reading can get the information.
- Form Accessibility: Forms should have clear labels, error messages that are announced to screen readers, and avoid timing requirements (e.g., if a session times out, allow easy resumption).