How AI Enabled Search is Changing SEO
Aimless browsing has its place. More often, we humans searching Google or Bing want results faster and with greater accuracy, whether it’s the best hiking shoes or million-dollar machines.
Enter, AI-enabled search, which is not all that new. Artificial intelligence for search has taken a quantum leap with the introduction of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, an artificial intelligence chatbot.
AI enhances the search experience to better understand what users really want when they type in their search or use voice commands. The underlying technology involves natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning.
For example, when a user searches for "best restaurants near me," this search engine can use NLP to understand that the user is looking for recommendations for nearby restaurants. The search engine can then use machine learning to analyze previous user behavior and search patterns to provide personalized recommendations for the user based on their preferences and location.
The Main Focus Of AI Search
AI search engines are increasingly focused on understanding the user's intent behind a search query. This means that SEO strategies that focus solely on keywords may become less effective. Instead, SEO will need to focus on understanding the intent behind a user's query and optimizing content to match that intent.
User Intent - Reading User’s Mind
The search engine's goal is to accurately interpret the user's intent and provide the most relevant and valuable results. Every search engine is striving to provide more useful and accurate search results. AI-enabled search engines use advanced algorithms to identify user intent and provide more relevant search results, which has significant implications for SEO.
These engines use advanced algorithms to analyze a user's search query and determine the underlying intent behind it. AI search engines use machine learning algorithms to improve their understanding of user intent over time. By analyzing user behavior and feedback, the search engine learns from previous interactions and improves its ability to deliver relevant results.
Here's an example of how user intent in AI search engines might respond to the search term “Apple” vs “Apples.”
| Search Results for "Apple"
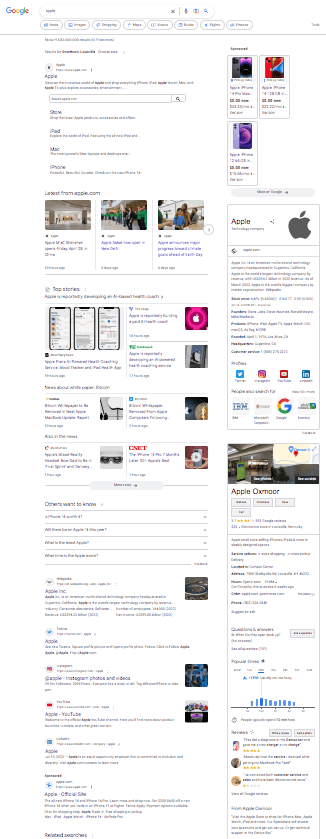
An incognito search on Google for “apple” returns search results all related to the technology company. Google’s vast data warehouse and algorithm reasoned the user's intention to be for the company. |
Search Results for "Apples"
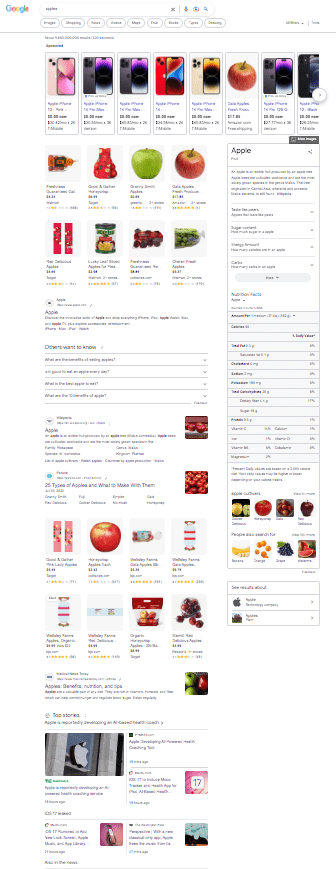
An incognito search on Google “apples” returns a mix of search results about apple, the fruit. Because of the uncertainty of the search term, Google also offered results related to the technology. |
Suppose a user searches for "Apple" on an AI-powered search engine. The search engine's algorithm will analyze the query's context, language, and structure to determine the user's intent. The algorithm might interpret the user's intent in various ways, depending on the search context. For example, if the user's previous search history or location suggests they want information about Apple products, the algorithm might show results related to the latest Apple iPhone or MacBook.
Similarly, if the user's search query is related to the history of Apple, the algorithm might show results related to the founding of the company or the biography of Steve Jobs. Alternatively, the user with a history of searches about baking may get results for the best apple for a pie.
In this way, the AI search engine can determine the user's intent and provide the most relevant and valuable results based on the user's needs and interests. Evolving AI analyzes the language used, the context of the query, and the user's previous search behavior to provide more relevant and accurate results that match the user's intent.
The Opportunities and Challenges of AI-Powered Search Results
As AI-powered search engines evolve, businesses and individuals must understand the opportunities and challenges they present to make informed decisions and effectively navigate the changing landscape of search.
Personalization
Search engines can now personalize search results based on a user's search history and behavior. This means that the same query could yield different results for different users, making it more challenging to optimize for a particular keyword. Personalization through AI-powered delivers more relevant search results based on user interests, behavior, and other data.
Search engines that incorporate AI into their algorithms can analyze vast amounts of user data, including search history, browsing behavior, and social media activity, to provide more relevant and personalized search results.
Suppose a user frequently searches for and clicks on articles about the latest Apple products. Based on this behavior, an AI-powered search engine may use personalization to show more results related to Apple products in future searches.
For example, if the user searches for "smartphone" on the search engine, the results may include more information and reviews about the latest Apple iPhone, as opposed to other smartphone brands. Additionally, the search engine may use personalization to display search results based on the user's location or search history. For instance, if the user is located in a city with an Apple store, the search engine may prioritize search results related to the store's location and offerings.
For a business to win in SEO, the content must be optimized beyond keywords. The content must consider user preferences and behavior. This results in a better search and user experience with information tailored to the user’s interest.
AI search engines can also deliver personalized ads to users based on their interests and behavior. This means that SEO strategies must work in tandem with paid advertising campaigns to ensure that both organic and paid search results are tailored to the user's interests.
Semantic Search
Semantic search engines attempt to determine the user's intent behind their query by analyzing the context and relationships between the words used in the search. It is a search technology that uses artificial intelligence and natural language processing (NLP) to understand the meaning behind a user's search query and provide more accurate and relevant search results.
The effect of semantic search on SEO is significant. In the past, SEO relied heavily on the use of specific keywords and phrases to optimize content for search engines. Semantic search understands the meaning behind a search query. SEO must shift towards creating content that is more relevant, valuable, and informative to users.
Here's an example of how semantic search might differentiate between two search queries related to "Apple":
Query 1: "Apple records" 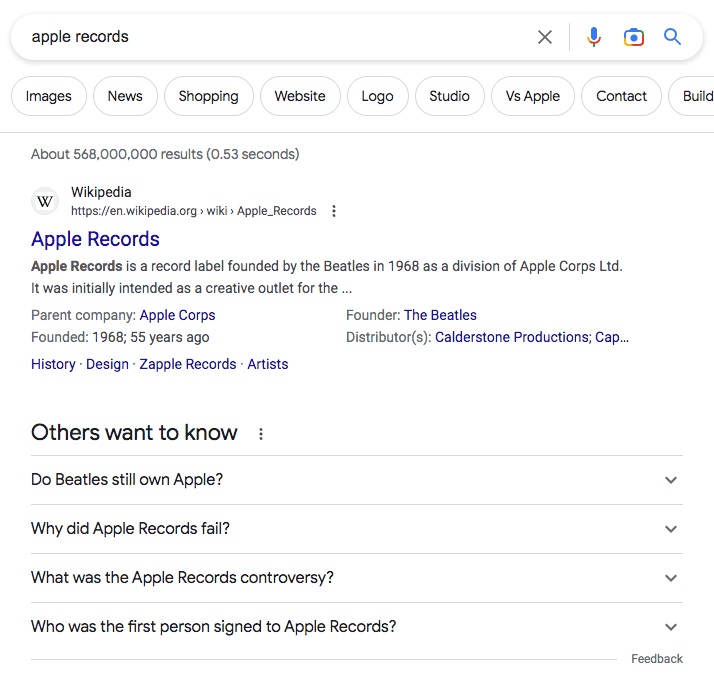
The semantic search algorithm will recognize that "Apple records" refers to a specific record label founded by The Beatles in 1968.
Therefore, the search results will likely display information related to the label's history, artists, and releases, as well as any news or updates related to the label.
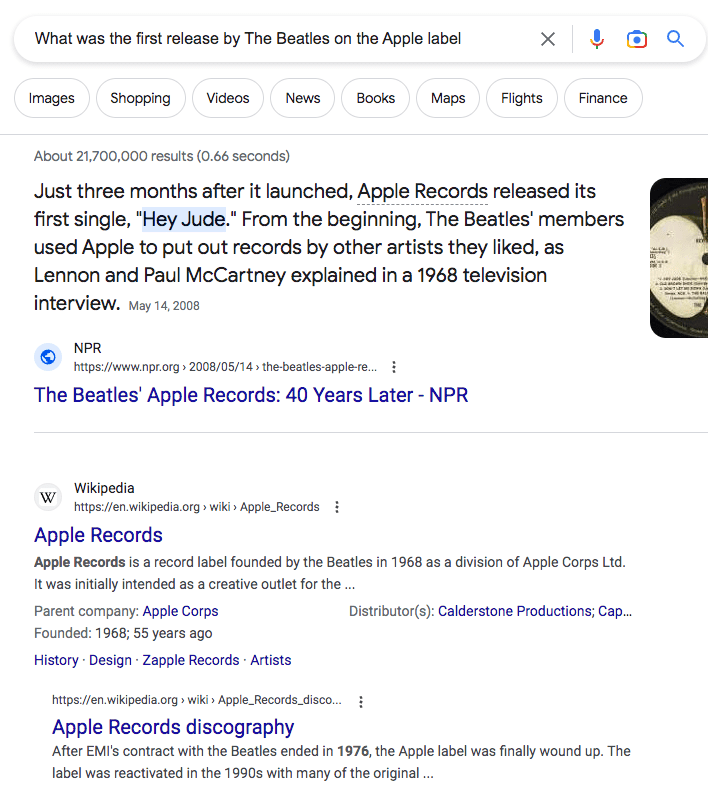
Query 2: "What was the first release by The Beatles on the Apple label?"
The semantic search algorithm will recognize that this query specifically asks for information related to The Beatles' first release on the Apple label. The search results will likely display information related to the label's history, the specific release, and any related details such as album art, track listings, and release date.
In this way, semantic search can differentiate between two seemingly similar queries and provide highly relevant and accurate results for each one.
 Semantic search has made it more important to create high-quality, relevant content that satisfies the user's intent behind their search. SEO now requires a more holistic approach that considers the keywords in relation to the context and intent behind those keywords. Businesses focus on creating content that satisfies the user's intent, improves their search engine rankings, and attracts more qualified traffic to their website.
Semantic search has made it more important to create high-quality, relevant content that satisfies the user's intent behind their search. SEO now requires a more holistic approach that considers the keywords in relation to the context and intent behind those keywords. Businesses focus on creating content that satisfies the user's intent, improves their search engine rankings, and attracts more qualified traffic to their website.
Clicks to a search result and subsequent visitor activity signal to the search engine to deliver this type of result more often when the content meets semantic parameters.
Voice Search
One of the primary effects of voice search on SEO is that it has led to a shift towards more conversational and long-tail keywords. When people use voice search, they tend to use more natural language and ask questions in a conversational tone. This means that businesses must optimize their content for longer, more conversational queries rather than short-tail keywords.
Here's an example of a voice search query for buying a used Apple phone: "Hey Siri, where can I buy a used iPhone near me?"
Siri will then provide you with a list of nearby stores or websites that sell used iPhones, based on your current location. For example, Siri might suggest checking out the Apple Refurbished Store, or other online retailers such as Gazelle or Swappa. Alternatively, Siri might provide a list of local secondhand shops or electronics stores where you can find a used iPhone.
Remember that the specific results may vary depending on your location and other factors.
Voice search has made it more important than ever to have a mobile-friendly website. Most voice searches are conducted on mobile devices, so businesses need to ensure that their website is optimized for mobile users. This includes having a responsive design, fast loading times, and easy navigation.
Snippets - For Quick Answers With Fewer Clicks
Another impact on SEO is the increased importance of featured snippets. When users ask a question using voice search, the search engine often provides a featured snippet in the search results that provide a direct answer to their question. Businesses can optimize their content to appear in featured snippets by providing clear, concise answers to common questions related to their industry.
Optimization: The Heavy Lift for Content Marketing
The days of low-hanging fruit to win at SEO are gone. Content optimized for search requires a precision and nuanced approach, a scalpel not a chainsaw.
AI-enabled search engines use sophisticated algorithms to analyze content and provide more accurate and relevant search results to users.
 One of the primary ways such search engines analyze content is by examining the text on web pages and identifying the most relevant keywords and phrases. This process involves analyzing the context of the words and phrases used, including their relationship to other words and phrases on the page.
One of the primary ways such search engines analyze content is by examining the text on web pages and identifying the most relevant keywords and phrases. This process involves analyzing the context of the words and phrases used, including their relationship to other words and phrases on the page.
AI search engines also analyze other factors, such as the structure of the website, the quality and relevance of external links, and user behavior signals such as click-through rates and bounce rates. These factors help search engines determine the overall quality and relevance of a web page and its content.
Schema markup is one tool for helping search engines understand content. Structured data is a core component of technical SEO, which drives online growth for businesses because it focuses on improving a website’s content and user experience at the code level to make it more friendly to both search engines and website visitors.
Earlier SEO used keyword stuffing to match the user’s search queries based on the most popular words used. That’s now a bad, bad thing that can land you in SEO hell. Later it progressed into the number of internal links and external links to your website or the bounce rates.
However, AI-enabled search is built to understand a user’s intent or understanding what the user actually wants. This means analyzing user behavior, understanding audiences, and having a voice and tone that connects with the audience. This leads to the next step in search optimization. Technical SEO further optimizes websites for search engine crawlers, ensuring that they are properly structured, organized, and easy to navigate. This includes optimizing the site's URL structure, using descriptive and meaningful title tags and meta descriptions, and also ensuring that the website is mobile-friendly.
Understanding User Intent Drives Success
The evolution or maybe the revolution of AI search shifts the focus to creating content relevant to the user's intent. Businesses must identify the user's intent behind their search query and create content that satisfies that intent. That’s what businesses do – identify needs or problems and offer a solution.
This means offering products, solutions, and high-quality content that engages and answers the user's questions or resolves their queries. By creating content that satisfies user intent, businesses can improve their search engine rankings and attract more qualified traffic to their website.
Focusing on user intent, optimizing for long-tail keywords, leveraging structured data, prioritizing mobile optimization, and embracing AI technology, drives improved search rankings. These SEO activities attract more traffic to your website, enabling you to stay ahead of the competition.
To know more, contact DBS.